We seek the best hedge fund strategies to meet your needs, whether they are focused on creating a portfolio with better resilience in bear markets or on generating absolute returns.
Gilles Flament
Global Head of Hedge Fund Strategies

Reducing sensitivity to unpredictable markets
Improving your portfolio’s risk-return profile
Using flexible and nimble investment techniques
Hedge Fund strategies outperform in equity bear markets
Comparison of the cumulative performance of Hedge Funds in the 5 worst equity bear markets between 1990 to 2022
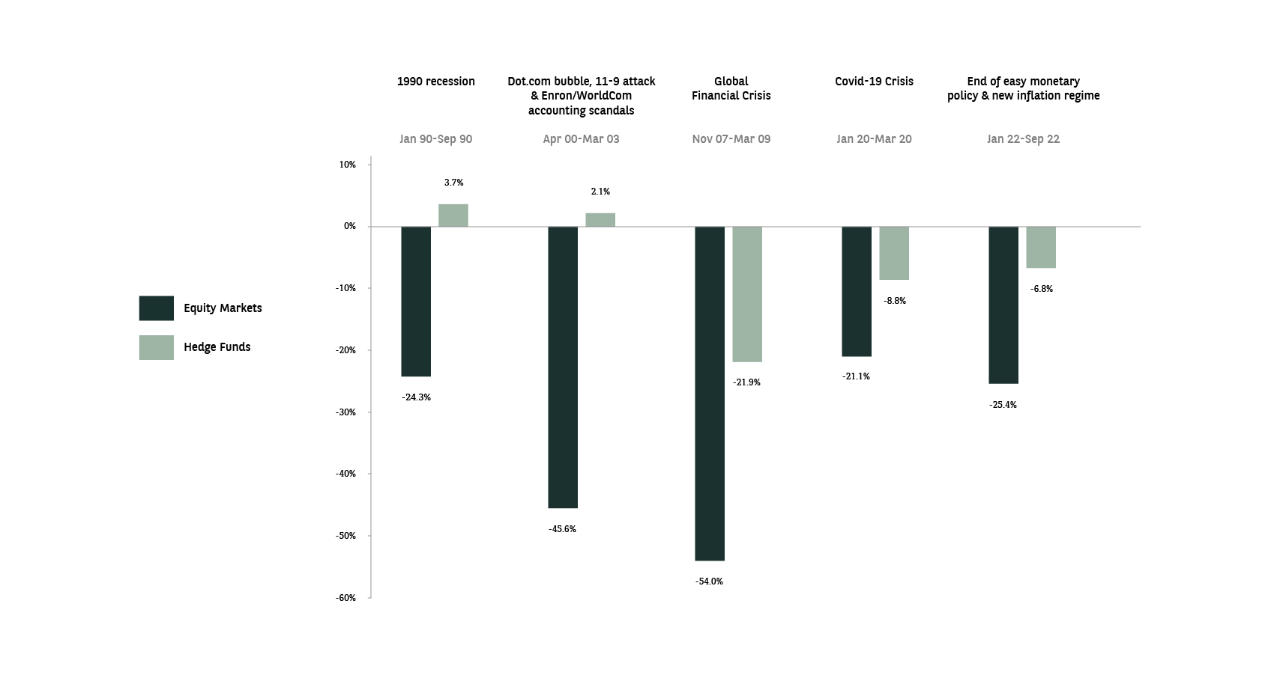
During the 5 worst (and most volatile) periods for equity investors since 1990, Hedge Fund strategies lost significantly less than global equity markets.
Equity markets: MSCI World TR USD; Hedge funds: HFRI Fund Weighted Composite USD; Source: Bloomberg
Past performance is neither a reliable indicator nor a guarantee of future results.
Improving your portfolio’s risk-return profile
Hedge Fund strategies are a complementary building block to your portfolio allocation
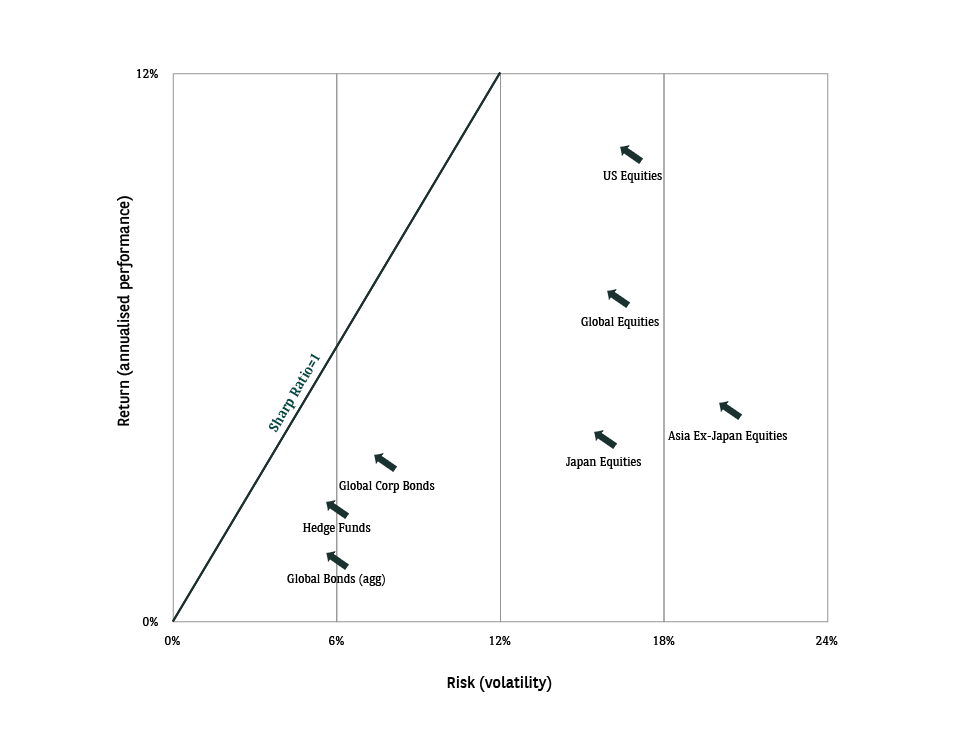
A comparison of different risk-reward profiles by asset class and geographical region versus a hedge fund index (from 30th January 2008 to 30th September 2022).
Hedge funds are a complementary investment style to traditional asset allocations and have a unique risk-return profile (i.e. the relationship between the amount of return gained on an investment and the amount of risk undertaken in that investment).
*HFRI Fund-Weighted Composite Index USD; Bloomberg Barclays Global Aggregate Corporate Total Return Index Value Unhedged USD; Bloomberg Barclays Global Aggregate Total Return Index USD; S&P500 TR; MSCI World Net TR; MSCI AC Asia Pacific ex Japan Net Total Return USD; MSCI Daily Total Return Net Japan USD.
Using flexible and nimble investment techniques
Long-Short Equity
A Long-Short Equity strategy involves taking long positions in stocks (buying “long”) which are expected to increase in value, and short positions in stocks (by borrowing stocks to sell them) which are expected to decrease in value (at which point the fund manager buys them back at a lower price than the amount paid, and returns them to the lender).
Global Macro
Global Macro managers seek to derive profits from changes in global economies that are brought about by changes in government policies that impact interest rates, unemployment and inflation, which then affect the currency, bond and stock markets.
Event Driven
This strategy focuses on capturing the value gap created when companies undergo transformative corporate events that have yet to be priced by markets but that are expected to have a significant impact on shareholder value. Investments can be made across the capital structure of a company (i.e. equities, corporate bonds, convertible bonds, etc.).
Relative Value
Fixed Income
We introduce the concept of arbitrage: managers simultaneously take long positions on securities which are underpriced and short positions on securities that are overpriced to make an incremental profit. A fund manager will apply this technique after having identified differences in the prices of various fixed income securities (e.g bonds that are quoted in multiple markets).

